A legal document follows a systematic hierarchical structure to ensure clarity, enforceability, and consistency. A legal document is structured logically and hierarchically, from broad legal principles (Title, Preamble, and Parts) down to specific details (Sections, Subsections, Clauses, and Tables). Understanding this structure helps in navigating complex legal texts efficiently and ensures clarity when studying or interpreting laws.
I extend my sincere gratitude and acknowledgment to Dr. Abdul Aziz Khan Niazi, from the Institute of Business & Management (IB&M), UET Lahore, for his invaluable assistance and insights in shaping this knowledge. His expertise in Corporate Laws and Taxation has greatly enriched the content, making it more relevant to contemporary taxation practices. This acknowledgment also highlights his continuous contributions to promoting awareness and fostering meaningful discourse on Corporate Social Responsibility (CSR), benefiting both the student and professional community.
For detail pl review the post
The following components define the general structure of legal texts:
1. Title & Preamble
- Title: The official name of the law (e.g., The Companies Act 2017).
- Preamble: States the objective and purpose of the law, explaining its intent.
2. Table of Contents / Index
- Lists the Parts, Chapters, Sections, and Sub-sections to provide a roadmap for navigating the document.
3. Parts & Chapters
- Laws are divided into parts and chapters that group related topics together.
4. Sections & Subsections
- Sections: Define specific legal provisions.
- Subsections: Further elaborate the provisions within a section, providing details.
Example:
Section I: Define specific legal provisions
- Sub Section 1: Short Title & Number
- Sub Section 2: Extent or Scope
- Sub Section 3: Commencement or Date of Implementation
Section II: Definitions
5. Subdivisions of Sections
- Clauses & Sub-clauses: Provide additional conditions or explanations.
- Provisos (Provisions): Special conditions or exceptions within a section.
- Paragraphs & Sub-paragraphs: Further division of content for clarity.
6. Hierarchy of Legal Provisions
- Primary Sections (I, II, etc.): Often contain general or definitional aspects of the law.
- Subsections (I, II, III, IV, etc.): Elaborate on the primary sections with finer details.
- Scope and Implementation Date: Specifies the jurisdiction and timeline of the law's effect.
- Distinctions (Exact Meaning of Words): Ensures legal clarity and prevents misinterpretation.
- Alphabetical Arrangement: Some laws categorize key definitions and terms alphabetically for easy reference.
7. Additional Legal Attachments
- Schedules & Annexures: Provide supplementary materials such as detailed procedural rules, exceptions, and specific guidelines.
- Tables: Used for organized representation of data, figures, or structured information to support legal provisions.
Fixed vs Variable Parts
- Fixed Parts:
- Heading, Subheading, Caption, Sections and subsections, Clauses and sub-clauses, Proviso (provisions), Paragraphs and sub-paragraphs
- Variable Parts: Schedules, Annexures, Tables
Sources of Law
- Islamic Law
- Anglo-Saxon Law (General principles)
Overview of Legal Framework
| Concept | Explanation | Examples |
|---|---|---|
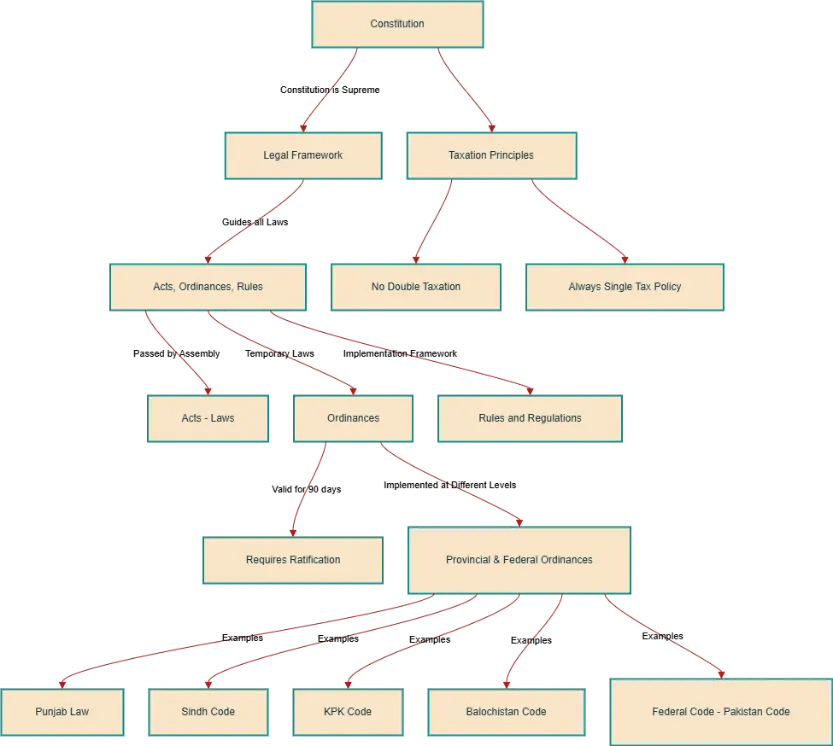
| Law vs. Constitution | The Constitution is the supreme law of the land; all laws must comply with it. | The Constitution of Pakistan |
| Taxation Principles | No double taxation; always follow a single tax policy to avoid over-taxing entities. | Income Tax, GST Policies |
| Understanding Laws & Acts | A Law = Act, passed by the legislative assembly and enforced as binding legal provisions. | Companies Act 2017, Income Tax Ordinance 2001 |
| Ordinances (Temporary Laws) | Laws issued by the executive government without Assembly approval, valid for 90 days. Require ratification. | President's Ordinance on Banking, Provincial Tax Ordinances |
| Implementation Levels | Laws may be implemented at Provincial or Federal levels. | Punjab Law, Sindh Code, KPK Code, Balochistan Code, Federal Code |
| Rules & Regulations | Frameworks that define the procedural aspects of Acts & Ordinances for enforcement. | SECP Rules, Tax Regulations, Banking Rules |
Legal Framework Presentation
Example Breakdown of The Companies Act 2017
The structure of The Companies Act 2017 follows the general legal format:
A. Preliminary Part (General Definitions & Scope)
- Section 1: Short Title, Extent, and Commencement – Establishes the law’s name, applicability, and enforcement date.
- Section 2: Definitions – Provides meanings of key terms used in the Act.
- Section 3: Application of the Act – Defines who is subject to the law.
B. Jurisdiction and Implementation
- Section 5: Jurisdiction of the Court – Specifies which courts handle company-related legal matters.
- Section 6: Procedure of the Court – Defines legal processes and appeals.
C. Business Formation and Regulation
Part IV: Incorporation of Companies
- Defines rules for registering a company.
- Specifies requirements for company names, registration, and legal structure.
Memorandum and Articles of Association (Sections 27-41)
- Outlines the constitution of a company, its objectives, and governance.
D. Share Capital & Ownership
Part V: Prospectus, Shares, and Debentures
- Covers the issuance, transfer, and regulation of shares.
E. Management and Corporate Governance
Part VII: Management and Administration
- Covers company meetings, directors' responsibilities, and legal compliance.
F. Financial & Taxation Rules
Accounts of Companies (Sections 220-238)
- Defines financial reporting, audits, and compliance with SECP regulations.
G. Winding Up (Liquidation of Companies)
Part X: Winding Up
- Covers dissolution procedures for failing companies.
How to Study Laws Efficiently
Identify Key Parts:
- Always start with the table of contents to get an overview.
- Focus on parts relevant to your subject (e.g., company formation, taxation, etc.).
Analyze Section Hierarchy:
- Read the main section first, then subsections to understand details.
- Identify definitions and provisos for clarity.
Cross-Reference Definitions & Schedules:
- Use the definition section (often in Section 2) to understand legal terms.
- Check schedules and annexures for additional explanations.
Understand Legal Language:
- Words like "shall" indicate mandatory provisions.
- Words like "may" indicate discretionary provisions.
Summarize with Examples:
- Try to rewrite sections in simpler terms to test your understanding.
Common Challenges in Studying Laws
| Challenge | Solution |
|---|---|
| Complex Language | Break into smaller parts; use simpler words. |
| Cross-References | Keep notes of connected sections for easy recall. |
| Long Documents | Use the Table of Contents to navigate efficiently. |
| Legal Jargon | Refer to definition sections and legal dictionaries. |
Mohsin Yaseen
On behalf of SolBizTech Team
Author of the article
https://www.linkedin.com/in/rmyasin