Corporate governance ensures that corporations are managed in a way that aligns with shareholder interests
I extend my sincere gratitude and acknowledgment to Dr. Safyan Majid, from the Institute of Business & Management (IB&M), UET Lahore, for his invaluable assistance and insights in shaping this knowledge. His expertise in Financial Management has greatly enriched the content, making it more relevant to contemporary finance practices. This acknowledgment also highlights his continuous contributions to promoting awareness and fostering meaningful discourse on Corporate Social Responsibility (CSR), benefiting both the student and professional community
For detail pl review the post
- https://solbiztech.com/blog/sbt-blog-1/the-role-of-financial-management-objectives-and-functions-13
- https://solbiztech.com/blog/sbt-blog-1/value-creation-agency-problem-and-corporate-social-responsibilities-in-financial-management-14
Corporate Governance refers to the framework of rules, relationships, systems, and processes within and by which authority in a corporation is exercised and controlled. It ensures accountability, fairness, and transparency in a company's relationship with its stakeholders (shareholders, management, employees, customers, and society).
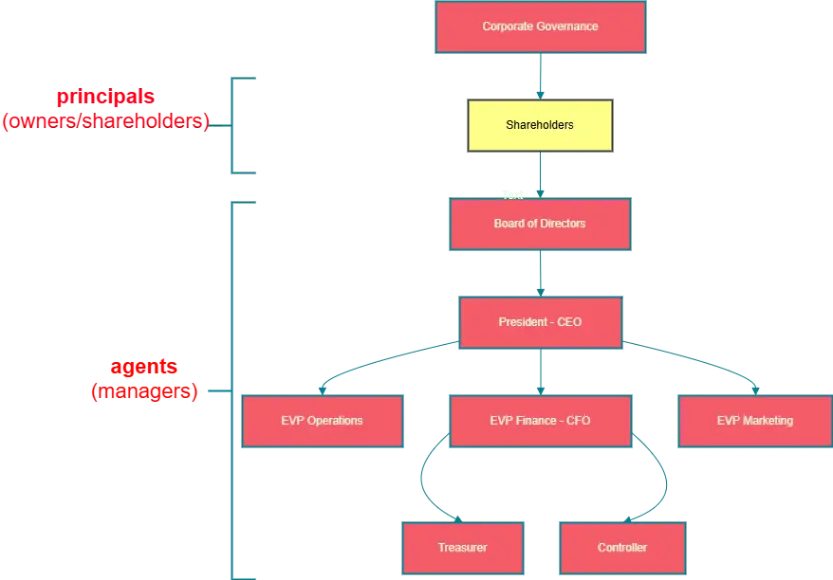
Key Elements of Corporate Governance
1. Shareholders (Principals):
- Shareholders are the owners of the company.
- Their primary role is to:
- Elect the Board of Directors.
- Approve major decisions such as mergers, acquisitions, or significant changes in the company’s structure.
- Shareholders act as principals in the principal-agent relationship.
2. Board of Directors:
- The governing body responsible for providing oversight and strategic direction for the company.
- They appoint the President (CEO) and ensure that management aligns with the shareholders’ interests.
- The Board is accountable to the shareholders for the overall governance of the company.
3. President (CEO):
- The CEO is the top executive responsible for implementing the strategies and policies set by the Board.
- The CEO bridges the Board of Directors and the executive management team.
4. Executive Management (Agents):
Executive management includes key roles like:
- EVP Operations: Responsible for day-to-day operational activities.
- EVP Finance (CFO): Oversees financial planning, resource allocation, and financial performance.
- EVP Marketing: Focuses on business growth, customer engagement, and market strategies.
5. Treasurer (Under CFO):
Handles financial resource management, including:
- Investment Decisions: Capital budgeting and pension fund management.
- Financing Decisions: Managing relationships with banks and investors.
- Asset Management: Handling cash flow and credit management.
6. Controller (Under CFO):
Focuses on financial reporting and compliance:
- Cost Accounting: Tracks and manages costs for efficient decision-making.
- Budgeting and Forecasting: Prepares and monitors budgets to ensure financial control.
- External Financial Reporting: Ensures compliance with regulatory bodies like the IRS, SEC, and shareholder communication.
Goals of Corporate Governance
- Transparency:
Ensure that all stakeholders receive accurate and timely information about the company’s operations, financial performance, and decision-making processes. - Accountability:
Hold the Board of Directors and management responsible for their actions and decisions, ensuring they act in the best interests of the company and its stakeholders. - Fairness:
Protect the rights of all stakeholders, including minority shareholders, by ensuring equitable treatment and opportunities for participation in corporate decisions. - Sustainability:
Align business practices with long-term economic, environmental, and social goals to ensure the company’s growth and success while contributing positively to society and the environment.
Mohsin Yaseen
On behalf of SolBizTech Team
Author of the article
https://www.linkedin.com/in/rmyasin